 Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is a critical digital marketing strategy that helps businesses and websites improve their online visibility and rank higher on search engine results pages (SERPs). In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the SEO process in detail, covering everything from keyword research to ongoing optimization.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is a critical digital marketing strategy that helps businesses and websites improve their online visibility and rank higher on search engine results pages (SERPs). In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the SEO process in detail, covering everything from keyword research to ongoing optimization.
1.Understanding SEO
Before diving into the SEO process, it’s essential to grasp the fundamentals of SEO. SEO is the practice of optimizing your website’s content, structure, and overall online presence to increase its visibility on search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo. The primary goal is to rank higher on SERPs, attract organic (non-paid) traffic, and ultimately, convert visitors into customers, subscribers, or readers.

2. Keyword Research
Keyword research is the foundation of any successful SEO campaign. It involves identifying the specific words and phrases (keywords) that potential users are likely to enter into search engines when looking for information, products, or services related to your website’s content. Tools like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, SEMrush, and Moz can assist in this process.

3. On-Page SEO
Once you have a list of relevant keywords, the next step is to optimize your website’s individual pages. This process, known as on-page SEO, involves:
a. Title Tags: Crafting unique and descriptive title tags for each page that include the target keyword.
b. Meta Descriptions: Writing compelling meta descriptions that encourage users to click on your search result.
c. Header Tags: Using header tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.) to structure your content and highlight important information.
d. Keyword Optimization: Naturally incorporating your target keywords into your content, headers, and meta tags without keyword stuffing.
e. Image Optimization: Using descriptive file names and alt tags for images to improve accessibility and SEO.

4. Content Creation and Optimization
High-quality content is the backbone of SEO. Search engines favor informative, well-structured, and relevant content. Here’s how to optimize your content:
a. Quality Content: Create content that answers users’ questions, provides value, and addresses their needs.
b. Keyword Integration: Incorporate target keywords strategically, maintaining a natural flow.
c. Long-Form Content: In some cases, longer, in-depth articles may perform better, but ensure they remain engaging.
d. Internal Linking: Include internal links to other relevant pages on your website to improve user experience and navigation.
e. External Links: Include authoritative external links to reputable sources to support your content’s credibility.
 5. Mobile Optimization
5. Mobile Optimization
With the increasing use of mobile devices, mobile optimization is crucial. Ensure your website is responsive and provides a seamless user experience on smartphones and tablets. Google’s mobile-first indexing means that Google predominantly uses the mobile version of your site for ranking and indexing.

6. Page Speed Optimization
A fast-loading website is essential for user satisfaction and SEO. Slow websites can lead to higher bounce rates and lower rankings. To optimize page speed:
a. Compress Images: Reduce image file sizes without compromising quality.
b. Minimize HTTP Requests: Reduce the number of requests by combining files and using browser caching.
c. Use Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): CDNs distribute your site’s content across multiple servers to reduce latency.
d. Choose Fast Hosting: Opt for a reliable and fast hosting provider.

7. Technical SEO
Technical SEO focuses on the behind-the-scenes elements that affect search engine crawling and indexing. Key aspects include:
a. XML Sitemaps: Create and submit XML sitemaps to help search engines understand your site’s structure and content.
b. Robots.txt: Use a robots.txt file to control which parts of your site search engines can access and crawl.
c. Schema Markup: Implement schema markup (structured data) to provide search engines with additional information about your content.
d. HTTPS: Secure your site with HTTPS, as it’s a ranking factor and essential for user trust.
e. Website Architecture: Ensure a clear and logical site structure with a user-friendly navigation menu.
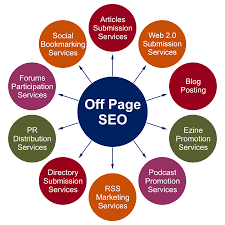
8. Off-Page SEO
Off-page SEO involves strategies and actions taken outside your website to improve its authority and reputation. Key elements include:
a. Link Building: Acquire high-quality backlinks from authoritative websites in your industry. Avoid spammy link-building tactics.
b. Social Media: Maintain an active social media presence to engage with your audience and promote your content.
c. Online Reputation Management: Monitor and manage your online reputation, addressing any negative reviews or comments.

9. Local SEO
Local SEO is essential for businesses serving specific geographic areas. Optimize your online presence for local searches by:
a. Creating a Google My Business (GMB) Listing: Ensure your GMB listing is accurate and up to date with your business information.
b. Local Citations: Consistently list your business’s name, address, and phone number (NAP) on various online directories and platforms.
c. Reviews: Encourage customers to leave reviews, and respond to them promptly and professionally.
 10. Monitoring and Analytics
10. Monitoring and Analytics
Regularly monitor your website’s performance using tools like Google Analytics and Google Search Console. Key metrics to track include:
a. Traffic: Analyze the volume and sources of your website traffic.
b. Rankings: Monitor your keyword rankings on search engines.
c. Click-Through Rate (CTR): Evaluate the effectiveness of your titles and meta descriptions.
d. Conversion Rate: Measure how effectively your website converts visitors into customers or leads.

11. Content Updates and Ongoing Optimization
SEO is not a one-time task; it requires continuous effort and adaptation. Keep your content fresh and relevant by:
a. Regularly Updating Content: Update and improve existing content to remain up-to-date and valuable.
b. Keyword Monitoring: Stay informed about changes in keyword trends and adjust your content accordingly.
c. Technical Audits: Conduct regular technical audits to identify and fix issues that may impact SEO.
12. Adaptation to Algorithm Changes
Search engines frequently update their algorithms, which can impact your rankings. Stay informed about algorithm changes and adapt your SEO strategy accordingly.
The SEO process is a multifaceted, ongoing effort that involves keyword research, on-page optimization, content creation, technical SEO, and off-page activities like link building and social media engagement. By following these steps and staying up-to-date with industry trends and search engine algorithms, you can improve your website’s visibility and drive organic traffic, ultimately achieving your online marketing goals. SEO is a long-term investment, and success often requires patience, persistence, and a commitment to delivering high-quality content and user experiences.
